Key Considerations for Implementing IFRS 17
The implementation of IFRS 17 has presented significant accounting changes, and its adoption will require close collaboration within insurance companies’ internal departments.
Outlined below are a few key considerations for the implementation of IFRS 17:
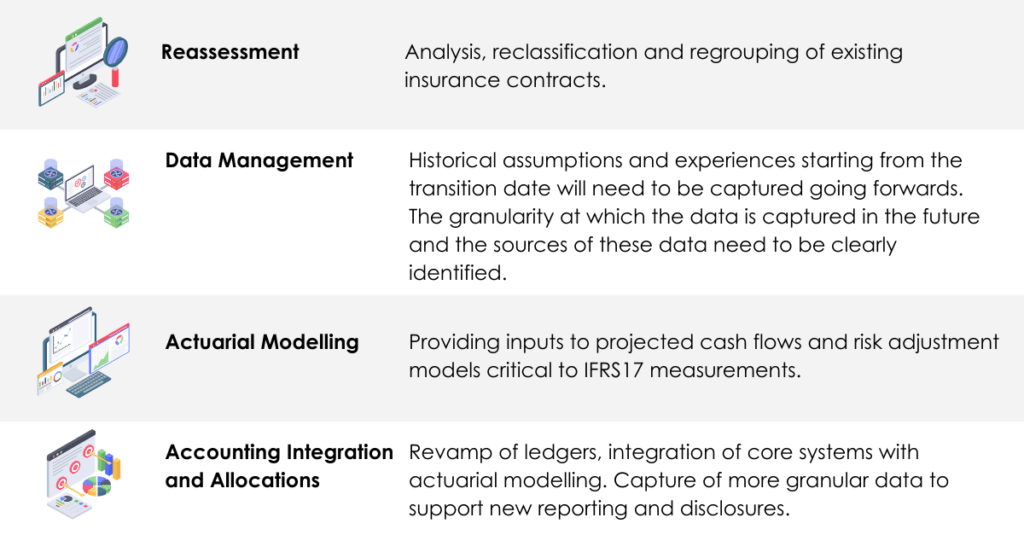
Insurance providers are monitoring the Standard as it evolves to ensure their data is analysed, new business processes are identified and preparing their technology platform to comply with the significant change.
IFRS 17 is the newest IFRS standard for Insurance Contracts, and it is being introduced to replace the interim Standard IFRS 4 Insurance Contracts issued in 2004. The IASB has recently deferred the implementation of IFRS 17 to 2023; this has been done to give insurers a realistic timeline to address the challenges that come with the new requirements that have been put forward.
IFRS 17 Insurance Contracts establishes 4 key principles with regards to the scope of Standard within insurance contracts, these being:
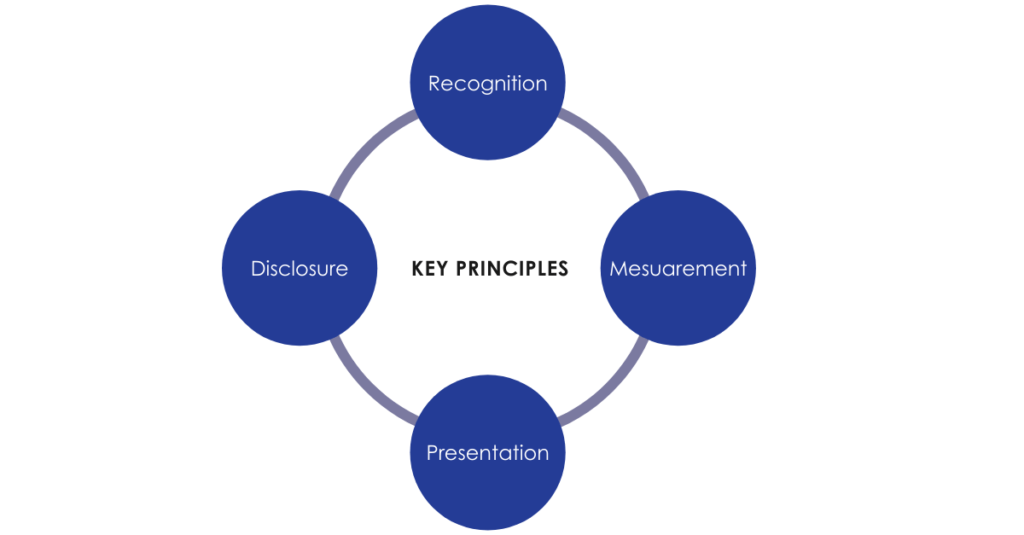
These 4 principles reflect the effect of any economic changes and enhance the comparability across insurers. The purpose of IFRS 17 is to ensure that a company is able to provide the relevant information that accurately represents those contracts. This information then allows users of this financial information to assess the impacts that insurance contracts have on a company’s cash flows along with both financial position and performance, enabling investors to have a better understanding within the sector.
Differences Between IFRS 4 & IFRS 17
The Issues with IFRS 4 and How IFRS 17 Addresses These
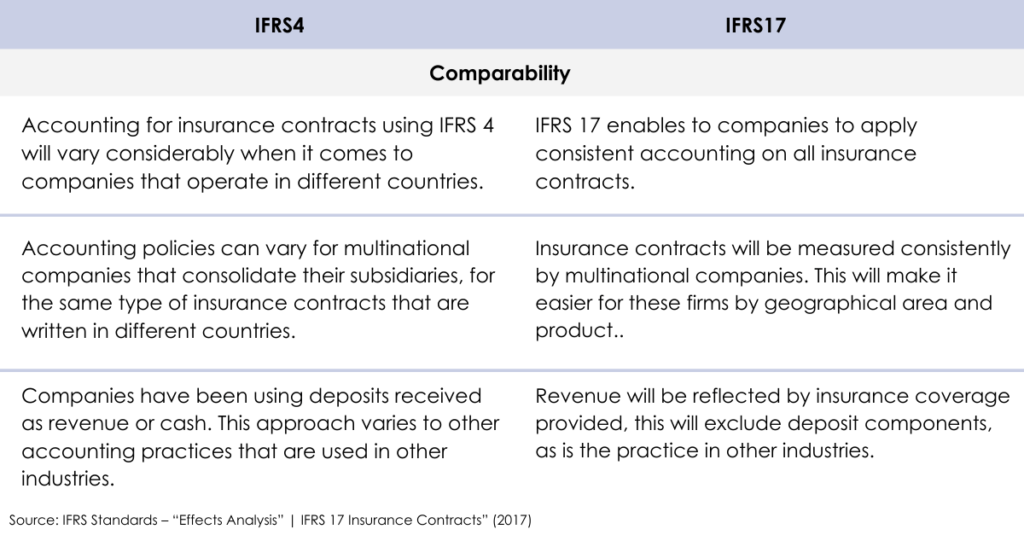
IFRS 4 was established in 2004 as an interim standard, with a view to there being little change to existing insurances practices. Insurers were still able to measure similar insurance contracts using different accounting policies when reporting on key aspects of their business. As these practices developed based on country-specific insurance contracts, gaps between accounting models used within the insurance industry and IFRS standards applied in other jurisdictions began to occur. This made comparability between insurance and non-insurance sectors extremely challenging, with investors and analysts finding it difficult to understand insurers results.
The introduction of IFRS 17 involves companies measuring insurance contracts through updated estimates and assumptions to remain consistent with current market information. These are then reflected on from the timings of cash flows (discount rate) and the uncertainty that surrounds insurance contracts (risk adjustment). Insurers are also required to indicate the expected profit with the Contractual Service Margin (CSM); this profit can then only be recognised once the insurance service has been delivered.
After all this information has been gathered, it should make it easier to evaluate the performance of different insurers against each other. Whilst offering one accounting model for all insurance contracts in all IFRS jurisdictions, facilitating consistent accounting on all insurance contracts. The new standard aims to equip investors with greater information about insurance contracts and exactly how each insurer is able to create value.
How Can VIP Apps Consulting Help?
With the right solutions and processes in place, the new Standard gives insurance organisations a great opportunity to implement quickly and elevate insights.
Our finance and technology consultants support finance teams with process optimisation, development of new business processes, data collections, technology consulting and reporting.



