The previous blog provided an overview of the principles of blockchain and distributed ledger technology, their different forms, benefits and drawbacks and a summary of potential areas for adoption. In this article, I’d like to highlight some emergent applications of this disruptive technology specifically within the Financial Services and FinTech sectors. The initial application of blockchain was related to cryptocurrencies, but whilst this is still relevant, this article will focus on other areas of use in Fintech and FS. There has been much recent investment by enterprises in developing blockchain-based applications and leveraging the power of distributed ledger technology in the real world. Any financial operation that has low transparency and limited traceability is vulnerable to disruption by blockchain applications. To gain competitive advantage in a crowded sector, FinTech companies are looking to leverage blockchains’ inherent strengths around improving data security, audit history and customer identity verification as well as reducing costs in the form of reducing costs for payment transactions and IT infrastructure. Whilst global blockchain data standards, providers and platform protocols are still developing, no financial service provider wants to be left behind in the race to deliver better service offerings and a richer customer experience, faster, cheaper and more securely.

FinTech is disrupting the traditional banking system by engaging with several different emerging technologies; blockchain is one element, but this can be integrated or complemented with other rising IT trends such as AI and machine learning and the Internet of Things (IoT). Many consider blockchain to be currently at the stage of the internet in the early 90’s; the range of applications for the technology and its potential in the era of digitisation are still being discovered. The trends for decentralisation of data, enhanced connectivity through open data exchange standards, increased regulation driving better ways to reduce fraud and cyber risks over current technologies and the rise of connected devices and smartphones are all factors that play to the strengths of blockchain and distributed ledger technology.
The growth of Blockchain in Financial Services
Due to the immense potential of blockchain and DLT for enhancing automation and digitisation, pressure to reduce costs and increase data security, the FS industry is already taking steps to develop real-world applications. Banks have been cautious to explore adoption of blockchain-based cryptocurrencies like Bitcoin due to well-documented issues around theft, fraud and links to criminal activity, but interest in the underlying technology itself grows. The disintermediation offered by blockchain, ie. the process of removing intermediaries and allowing direct ‘trustless’ transactions between the funding provider and recipient without a central authority, means financial services providers need to change the face of their services to avoid losing their ‘middlemen’ position and revenue streams to blockchain disruptors.
2019 should see further investments in experimental proofs of concept and more practical solutions of how it can be applied to help businesses and individuals. According to a report from Santander, by 2022 banks could potentially save US$20 Billion per year using blockchain to reduce infrastructure costs related to cross-border payments, securities trading and compliance activities. McKinsey & Co predict that blockchain will drive savings of $50 – $60 billion in cross-border B2B payments, and $3 – $5 billion in cross-border P2P payments. Per the Global Fintech Report (2017), 77% of Fintech institutes expect to adopt blockchain as part of their production system or processes by 2020.
KPMG, a company providing audit, tax and advisory services, released its ‘2019 Technology Industry Innovation‘ survey, which looked at responses from over 740 global leaders in the technology industry from 12 countries:
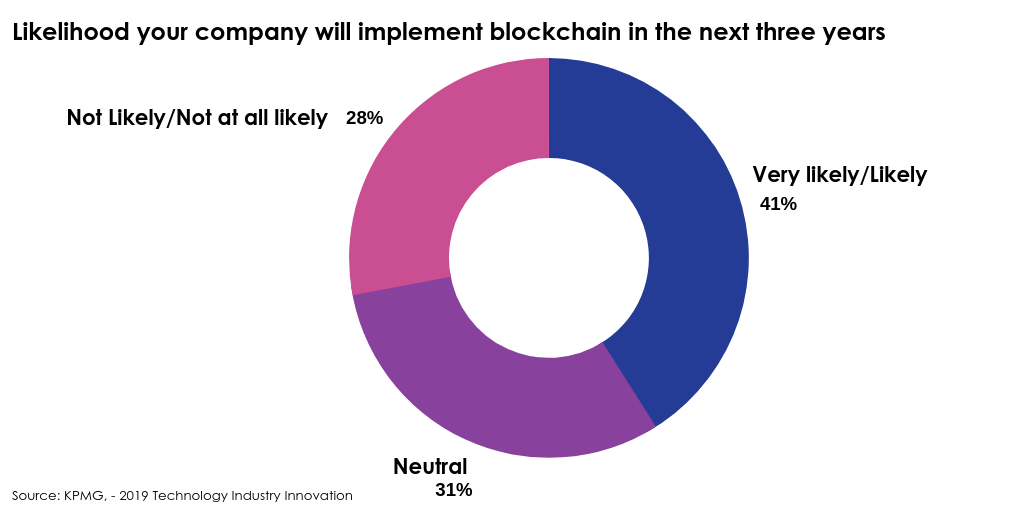
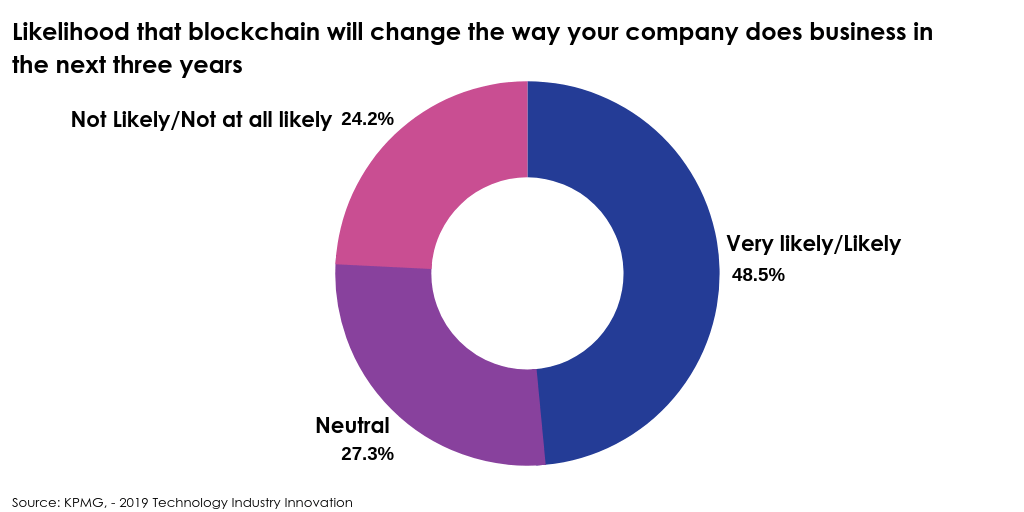
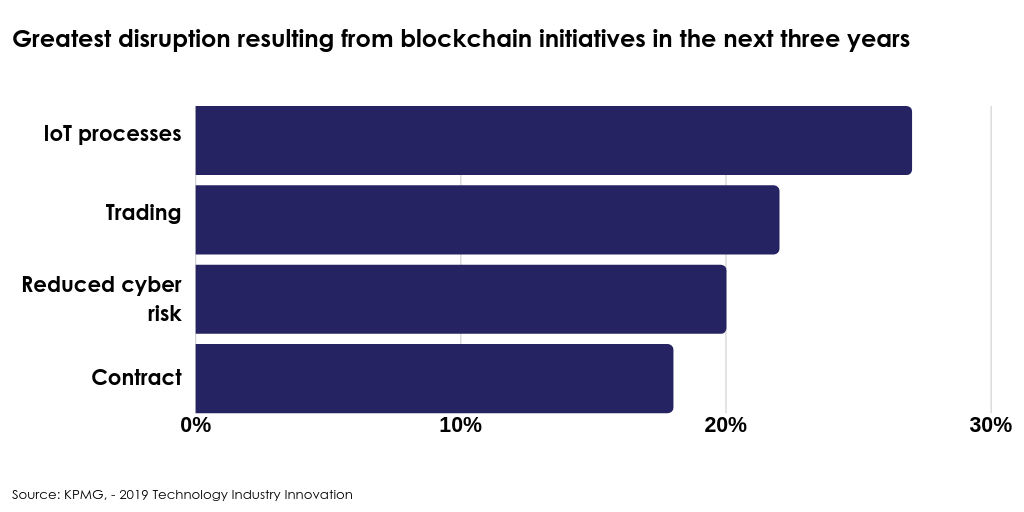
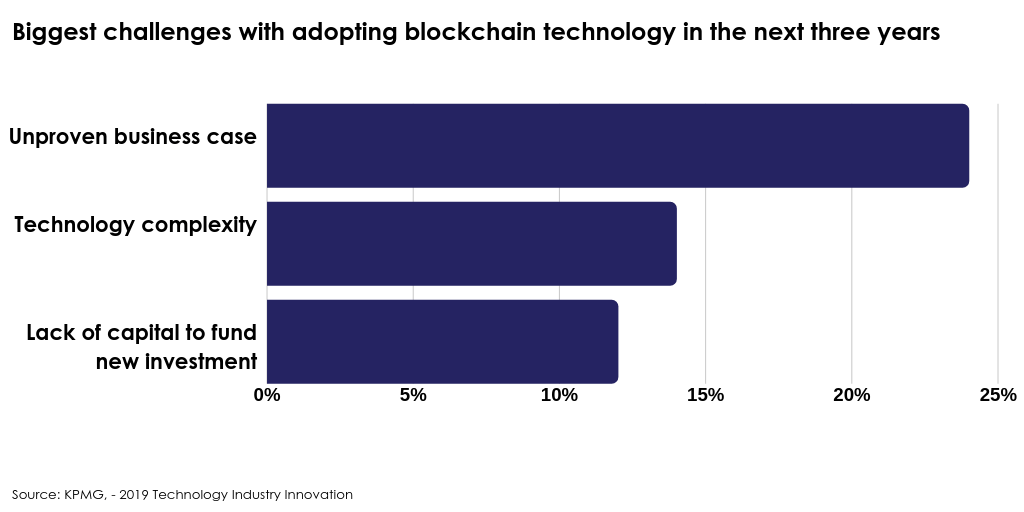
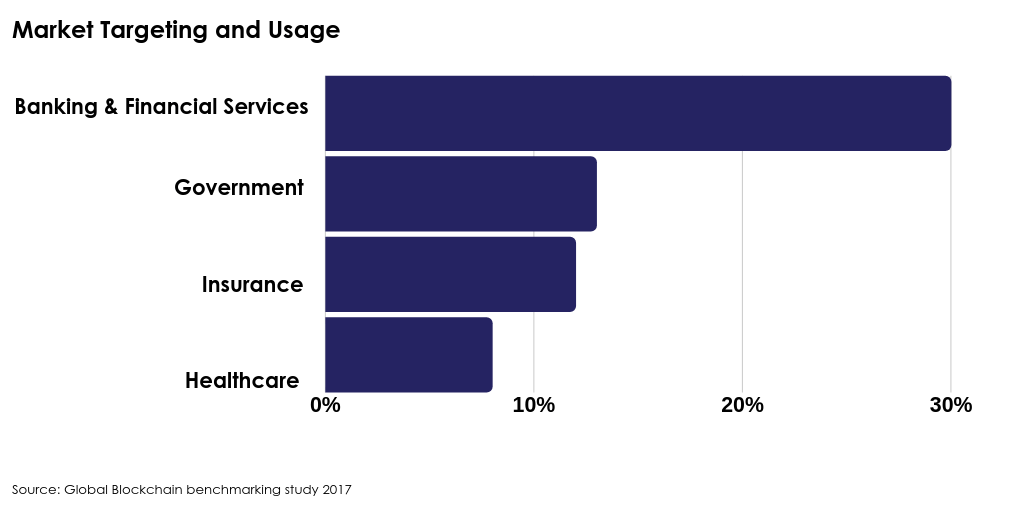
Current Blockchain Developments in FS and Fintech Domains
Commercial Banking and Capital Markets:
• Real-time loan funding and ongoing servicing with automated acceptance and fulfilment via smart contracts.
• P2P and Syndicated lending.
• Securities and stock trading clearing and settlements. The exchange of funds and securities between purchaser and seller currently involves a network of intermediaries, including market makers and brokers, clearing houses, depositories and stock exchanges. Blockchain can enable direct source to target fulfilment and permanent tamper-proof transactional history to be permanently created which is secure, fast and low cost.
• Currency and derivatives trade execution and liquidity management
• Post-trade compliance (reconciliation, reporting) – immutability of transaction history keeps auditors happy and distributed ledgers means both source and recipient trade data is held on the same distributed ledgers, meaning errors between different ledgers and reconciliation should be easier.
• Asset transfers, registry management and servicing
• Client loyalty program management – blockchains’ low transactional cost and security should enhance the ability to manage loyalty programs which are often seen as good for customer experience and thus loyalty but high in cost due to administration of high volume but low transactional values
Payments:
• Cross border and fiat FX currency payment transfers, virtual wallet and cashless facilities
• Wholesale and P2P payments – though Bitcoin is the largest application of blockchain, given the reputational issues businesses are venturing into affordable cross-border payments. Circle is a popular bitcoin app that shifted to the P2P payment model
• Microcredit facilities and microloan payments – blockchain fintech startups have already emerged to cater for P2P micro-payments, eg. Sentbe and Abra, who offer a cheaper service for sending money abroad and offer cash collection locations as an alternative to traditional card/bank transfers – very attractive for the underbanked or unbanked population, particularly when combined with easy personal access to the services through secure mobile banking apps
Risk Management:
• Identity management and theft protection, KYC and onboarding – some major financial services providers like IBM, SecureKey, HSBC, Deutsche Bank and Santander are using blockchain to place their customers’ identities on it as well as developing a blockchain system for trade finance. Blockchain would allow the independent verification of a client by an organisation which could then be accessed by other organisations to avoid costly repetition of the KYC process
• Risk audit and compliance reporting
• Identification of source of funds and anti-money laundering
• Counterparty risk management
• Liquidity risk management, solvency tracking and bankruptcy detection
Regulatory Compliance:
• Automated compliance activities (eg CCAR related)
• Regulatory reporting (eg AML, KYC, CDD)
• Audit trail for compliance verification – DLT can be leveraged by banks as the transparency of information and permanence of records makes it virtually impossible to allow executed transactions to subsequently be altered. Banks no longer have to keep redundant audit trails of transactions, as the encrypted data links in the blockchain forming the transaction ledger is the audit trail
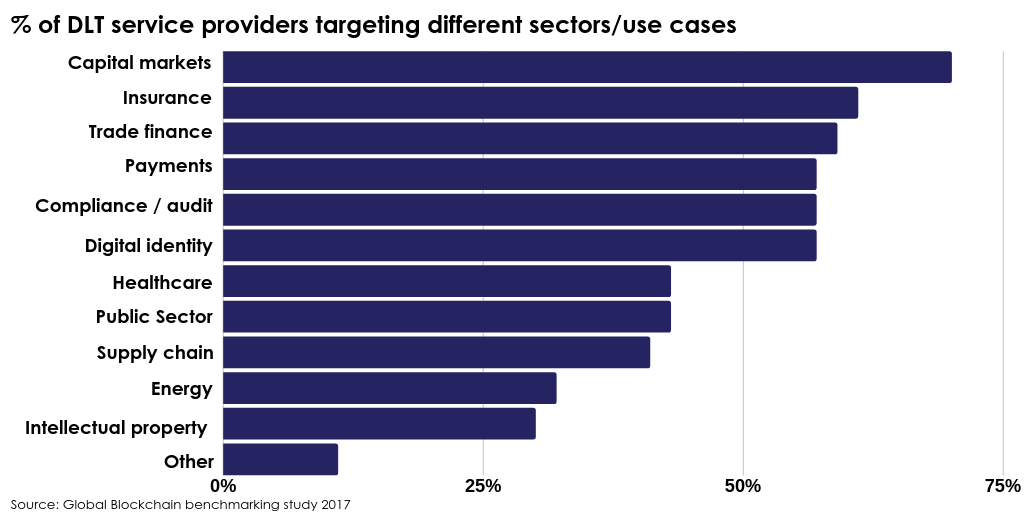
The Global Blockchain Benchmarking study 2017, the survey data confirms the use case in financial services, payments, and banking services are the most frequently targeted sectors:
Summary
As can be seen, the financial services sector is investing heavily in blockchain and DLT to ensure they maintain their position in the market and keep ahead of the curve with employing emerging technology for competitive advantage. FinTech startups are smaller, don’t have the hard-to-change legacy IT infrastructure of the established banks and can therefore be more agile in adopting this new technology, but need to attract funding to cover the time to market for developing and implementing their services. In a competitive sector with many new entrants and cutting-edge technologies forcing change continuously, FinTechs need a strong service offering differentiator to stand out. Traditional banking is looking for evolution of their existing banking infrastructure, whilst FinTech can potentially offer revolution here and now. Time will tell who succeeds.
Blockchain could be a powerful tool, but organisations must have an aligned, clear vision of their future technology strategy. Blockchain has the potential to reshape the way business operates and challenges organisations to reimagine their business processes and customer experience. It presents an excellent opportunity to start building a more efficient, secure and sustainable operating model that will enable the adoption of innovative technology.
Next
This article looked at blockchain for the financial services and FinTech sector – in the next article, I will focus further specifically on the leasing and asset finance industry, and how the technological advantages offered blockchain and distributed ledgers can be leveraged by lessors and asset funders.
About the Author
Financial Application Consultant and Project Manager with 20 years experience of consulting and delivery of financial and accounting transformation initiatives across sectors such as Retail and Investment Banking, Leasing and Asset Finance and other Financial Services. Peter has executed lead roles on numerous ERP and finance systems transformation programmes. His excellent client facing communication skills add to core strengths in project management, business process analysis, system selection and implementation, accounting design, data migration and reconciliation.
VIP Apps Consulting provide business process management and technology consulting services. We develop and implement unique solutions to enable organisations to address their challenges and become high-performance businesses, creating value through innovation and process optimisation.
We operate in the intersection of technology and business, combining deep business and industry insight with the understanding of how technology and innovation impact the industry and business models.
Get more insight like this
in your inbox
Subscribe to our mailing list and get industry and technology insights and updates to your email inbox.
Thank you for subscribing.
Something went wrong.
The form collects name and email so that we can add you to our newsletter list for updates. Checkout our privacy policy to learn how we protect and manage your submitted data.





