ERP systems provide an integrated suite of applications for an enterprise to manage resources, control supply, purchasing and sales operations and provide operational and financial control of the business. Applications would typically include Inventory and Supply Chain Management (SCM), Customer Experience (CX), AP, AR and Financials and human resource management. This article will look at how blockchain technology is being augmented with ERP systems to open up enterprise boundaries and reduce inefficiencies and security risks between businesses, their suppliers and consumers.
Blockchain Integration With ERP Systems – an Evolution
Blockchain technology was originally centred around cryptocurrencies, but the underlying technology of providing trustless, disintermediated transactional execution with an immutable, visible record history presents many potential benefits to ERP systems. ERP software providers such as SAP and Oracle have been investing in developing blockchain applications in areas such as manufacturing, logistics and supply chain, payments processing and identity management. This ‘additive’ approach of using connectors or modules for existing ERP applications to access blockchain networks is therefore seen as an evolution in the short term to further advance digitisation in ERP systems. In the longer term, blockchain applications may fully replace ERP modules themselves as technical and regulatory standards stabilise and widespread business adoption reaches critical mass.
The main difference in adopting blockchain applications to using the traditional siloed single enterprise-wide ERP installation is one of commitment to opening processes and data transaction execution and visibility wider than just up to the organisation’s firewall. Blockchain requires businesses and trading partners to extend their trust boundaries to allow peer-to-peer transaction approval and execution, enabled by smart contracts defining pre-agreed fulfilment rules with approved partners across a private or hybrid private/public blockchain network.
ERP System Transactions and How Blockchain Can Automate
Let’s take a simple example – a wholesaler raises a purchase order to a manufacturer. The manufacturer creates a sales order, fulfils the order and ships the item to the wholesaler. The ERP transactions at a simple level would be:
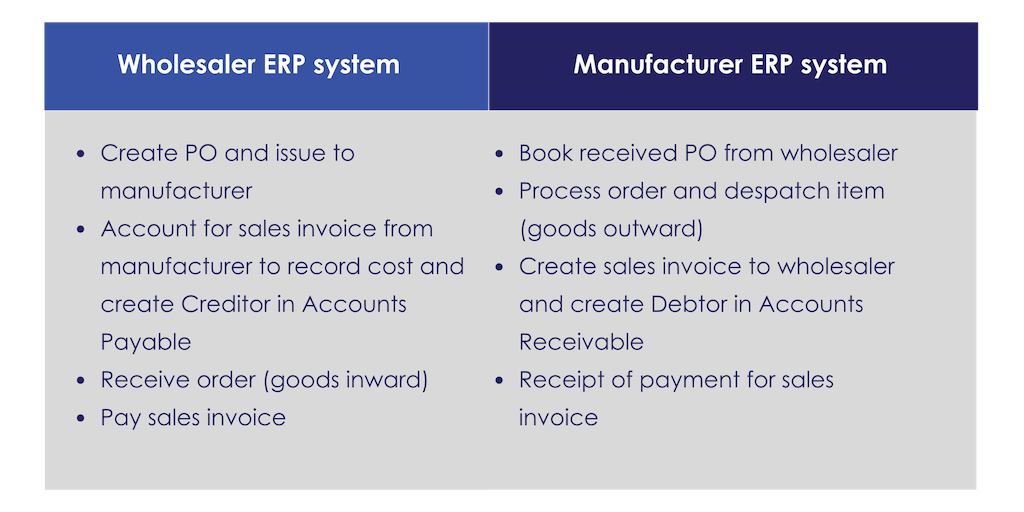
The above model does not include the myriad of other transactions and processes followed within each company’s ERP system for tracking orders in process, credit management, logistics, cash management, time and materials recording, etc, and also assumes the supply chain is just between two enterprises and not using multiple trading participants. The transactions are recorded by both companies in each of their ERP systems, effectively mirroring each other with resulting duplication of effort, leading to inefficiencies of time, cost and potential risks from fraud or error. Both parties would need to reconcile the transaction within their own ERP systems to ensure integrity and accuracy.
Let’s think how blockchain connectivity and use of smart contracts between the companies could be applied reduce these inefficiencies: assume there is a private blockchain network for these supply chain participants, with smart contracts defined for automated transaction processing when order/fulfilment rules are met, agreed and trusted by both parties.
The transaction boundaries between wholesaler and manufacturer are therefore opened up and data shared, simultaneously. When the order is placed by the wholesaler and accepted by the supplier, the transaction execution is automated and recorded simultaneously by both parties. This removes any processing time lag or possibility of recording error on either side. Both parties will report the transaction in their ERP systems, knowing it is valid (as execution conditions pre-agreed) and unalterable after being recorded securely with encryption in the blockchain and therefore should remove the need for validation or reconciliation. The transactions created for invoicing and transfer of payment after pre-agreed fulfilment conditions are met will also benefit from blockchains’ advantages of shared data providing synchronous transaction reflection in both ERP systems with increased security and removal of costly inefficient processes and checks.
Supply Chain Management and Blockchain – the Perfect Marriage?
SCM is often cited as the ideal area of blockchain application, utilising its inherent strengths of data visibility, speed, identity security and creation of a tamper-proof record trail of all supplier and goods/services interactions through the supply chain processes. Blockchain has the potential to integrate an end-to-end record of the same supply chain, using a shared decentralised system, facilitating provision of various types of information, from the specifications and sources of manufacturing inputs to details about the precise machine that made a product. The tamper-proof nature of blockchain record keeping and identity management for approved participants also provides reduction in risks.

Full visibility for participants within the supply chain can be made available on product genealogy and provenance at each stage up to the final consumer, helping to identify supplier and materials sources of finished goods for regulatory compliance, defect or contaminant control, as well as to eliminate counterfeiting. End-to-end tracking of materials, manufacturing processing and delivery logistics in a single supply chain can provide useful information on the resources consumed, pollutants created or carbon footprint of finished goods. Suppliers at various stages in the chain can use the trail of data to identify more ecologically efficient suppliers or materials. Using Smart contracts to auto-execute supply chain transactions according to agreed rules can also remove the human element to reduce errors, increase data recording speed to near-real time and therefore assist with just-in-time manufacturing processes.
Payments – Fast, Cheap and Secure
Blockchain has already demonstrated real-world advantages for B2B and B2C payment transactions, enabling payment transactions with lower costs, increased security and speed, particularly for international payments. A blockchain-based transaction can be completed in seconds or minutes at a fraction of the cost – for example, international payment transaction costs using blockchain are often cited at around only 5% to 10% of the current typical wire transfer charge levied by banks. Disintermediation facilitated by blockchains’ direct peer-to-peer transactional processing removes inefficiencies in time and cost for moving money between parties, and the transactions are securely stored in an unalterable way in the blockchain in a way that is visible to all authorised participants to the transaction, something auditors love.
Human Resource Management – Identify Yourself
Human resource management in ERP systems can also utilise the advantages blockchain has to offer. Resource on-boarding can utilise blockchains’ inherent identity management advantages for ERP access for internal and external resources. The immutable record trail in the blockchain can be used securely track work assignments and project time recording, across enterprises. It is worth noting that the use of storing identifiable human resource data on the blockchain can require compliance with GDPR regulations.
Asset Management
Assets employed by businesses need to maximise their investment cost by being as fully utilised as possible, with minimum downtime from unplanned repairs and maintenance. By leveraging the use of blockchain networks with IoT connectivity, artificial intelligence (AI), and machine learning, asset users can gather reliable intelligence from physical assets via sensors. This information can then be used to plan for asset maintenance and schedule replacements or upgrades to avoid costly downtime due to equipment failure or suboptimal asset usage.
Why Is Blockchain Important for ERP Systems
Blockchain has the potential to transform ERP system interactions and record sharing between businesses in the areas discussed above. It enables a trusted business network to transact directly over a peer-to-peer network while still ensuring the validity and integrity of the transactions and removing costly and time-consuming duplication of effort and validations. Adoption requires a major shift in the willingness of participants in the blockchain network to open up their boundaries from the current single enterprise installation model to a shared distributed network. Trust for executing transactions and visibility of records across distributed ledgers requires a paradigm shift to reap the potential benefits blockchain technology offers. To reduce risk, businesses are favouring private blockchains restricted to authorised participants, but avoiding use of public blockchain networks reduces the full potential that can be gained by allowing enterprises to connect and transact easily and securely, globally. A hybrid blockchain solution of using part-private and part-public networks may provide a reduced risk approach to global connectivity.
What is sure is that investment in blockchain capability by ERP software suppliers is continuing to grow and gain interest. Experts say it could potentially transform how businesses use ERP systems to interact and operate in the future. Early adopters may get a competitive advantage in the continuing journey towards automation and digitisation.
About the Author
Financial Application Consultant and Project Manager with 20 years experience of consulting and delivery of financial and accounting transformation initiatives across sectors such as Retail and Investment Banking, Leasing and Asset Finance and other Financial Services. Peter has executed lead roles on numerous ERP and finance systems transformation programmes. His excellent client facing communication skills add to core strengths in project management, business process analysis, system selection and implementation, accounting design, data migration and reconciliation.
VIP Apps Consulting provide business process management and technology consulting services. We develop and implement unique solutions to enable organisations to address their challenges and become high-performance businesses, creating value through innovation and process optimisation.
We operate in the intersection of technology and business, combining deep business and industry insight with the understanding of how technology and innovation impact the industry and business models.
Get more insight like this
in your inbox
Subscribe to our mailing list and get industry and technology insights and updates to your email inbox.
Thank you for subscribing.
Something went wrong.
The form collects name and email so that we can add you to our newsletter list for updates. Checkout our privacy policy to learn how we protect and manage your submitted data.